Panaya test automation enables creating and using a variety of data types and to support adding logic, dynamic parameter values, and conditional behavior into your automated scripts. These expressions help you calculate values, compare fields, and control flow using operators, functions and parameters.
Whenever your data includes something which is more than just a simple “string”, you can use Expressions to -
Validate expected results.
Perform conditional checks.
Reference field values dynamically.
Apply simple formulas or transformations.
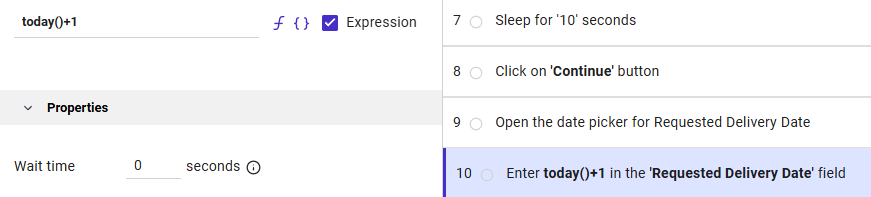
When using functions, parameters, operators and integers, make sure to check the Expression checkbox. In that case, a string should always be entered inside single quotes e.g. ‘string’.
You can also use the following operators to implement more sophisticated logic to your script:
Basic Operators
You can perform calculations or comparisons.
Math: +, -, *, /
Example: {Amount} * 0.15Comparisons: =, <>, <, >, <=, >=, !=
Example -
{Status} = ‘Approved’
Note
To validate whether a field is empty, compare it to an empty value.
Example -
{Status} = ''
Logical Operators
Combine multiple conditions.
AND, OR, NOT
Example -
{Amount} > 1000 AND {Region} = ‘EU’
Note
1. Comparison Operators
To compare a field or variable against a specific value, use standard comparison operators (e.g.,
>,<,=).
Example:
{x} > 5Example:
{y} < {z}2. Logical Operators
The system supports the primary boolean operators: And, Or, and Not.
Operator: Usage Requirement: Example:And Must have a boolean expression on both sides. {x} > 5 And {y} < {z}
Or Must have a boolean expression on both sides. ({x} = 4) Or ({y} = 8)
Not Must have a boolean expression on the right side. Not ({x} > 5)
3. Working with Multiple Values (
InFunction)When checking if a single field matches one of several possible values, you can use the
Infunction. This is often more concise than using multipleOrstatements.
Standard Syntax (Or):
({x} = 4) Or ({y} = 8)Shorthand Syntax (In):
In({x}, 4, 8)4. Best Practices
Parentheses: Always use parentheses when using the
Notoperator or when nestingAnd/Orconditions to ensure the correct order of evaluation.Field References: Ensure all fields are enclosed in curly braces (e.g.,
{FieldName}).Case Sensitivity: Logical operators (
And,Or,Not,In) are typically treated as keywords; ensure they are formatted correctly to avoid issues.